Agilent Corporate Citizenship Report 2014

DMA EN
DISCLOSURE ON MANAGEMENT APPROACH EN
Agilent is committed to conducting its business in an ethical, socially responsible, and environmentally sustainable manner by reporting performance and ensuring that production and operations meet or exceed relevant environmental legislation and regulations. We operate under a company-wide Environmental, Health and Safety Management System (EHSMS) that applies to our design, development, manufacturing, distribution, and sales and service operations worldwide. Agilent has demonstrated its effectiveness in managing environmental impact by maintaining an ISO 14001 registration of our EHSMS. EHSMS is a tool to drive continual improvement in environmental performance and pursuit of sustainability. We expect our suppliers to adhere to the same standard of environmental and social responsibility that we maintain, and our Supplier Environmental and Social Responsibility Code of Conduct Policy requires suppliers to adopt sound environmental, health, and safety management practices.
Agilent Supplier Code of Conduct Policy
Agilent is committed to designing, manufacturing, and distributing environmentally responsible products. Environmental aspects are considered in the design, manufacture, distribution, use, obsolescence, disposal, recovery, and reuse of Agilent products. Our aim is to minimize environmental impact of our products and operations by conforming to applicable regulations. Agilent has developed an Environmental Compliance Framework to sustain and facilitate compliant product design, development, production, refurbishment, and support. When a customer no longer requires an Agilent product, we have implemented several options for reuse, remanufacture, or take-back based on the product type and customer location to ensure the product is properly managed. Additional information on our environmental and social performance may be found at Agilent's Commitment to Environment and Social Responsibility.
Agilent is working on improving the energy efficiency of selected products/product families compared to the predecessor models. Product families include instruments with high energy consumption. Agilent has worked on assessing energy efficiency of several types of products by using customer base metrics. By identifying energy-using features, we are able to increase energy efficiency of our products. During the past several years, Agilent has moved toward increasing product energy efficiency in several product lines. Most of the energy savings are due to two key factors: 1) The increased type and volume of tests that can be conducted, thus increasing tests per watt. 2) Enhancement of existing product features, thus bringing more measurement capabilities to the same product footprint. Agilent's concentration on handheld and portable instruments places a focus on energy efficiency: Next-generation products are using key new technology that greatly improves performance per watt of power supplied. Agilent puts significant power management design efforts into its portable products to achieve power, heat, and battery life targets. Industry and regulatory requirements on the power supplies for our portable products have also increased power supply efficiency.
Agilent aims to minimize the environmental impact of our products and operations:
- Products are designed to be highly reliable to maximize their useful life.
- Maintenance and repair services extend the useful life of Agilent products.
- Customers benefit from product upgrade, trade-in and trade-up programs.
- Reuse programs are offered for selected products, also addressing requirements from the European WEEE (waste from electrical and electronic equipment) Directive.
Protecting People and Our Environment
Environmental testing and food safety are significant applications of our products. Offering measurement capabilities in these areas is one of the many positive environmental impacts of Agilent products. Our instruments, systems, and supplies are used throughout the food production chain, including incoming inspection, new product development, quality control and assurance, and packaging. This includes applications in:
- Pesticides and mycotoxins and other contaminants and toxins
- Veterinary drugs
- Food processing and packaging
- Food authenticity
- Dietary supplements and natural compounds and additives
- Soil quality and fertilizer analysis
Agilent also provides market-leading solutions for the determination of organic and inorganic contaminants in air, water and soil as well as products that enable the development of cleaner, more efficient and alternative fuels.
- GC and GC/MS
- LC and LC/MS
- ICP-MS
- Automation
Energy and Water Conservation Achievements
Agilent continues to implement energy and water conservation initiatives across the company. These initiatives include capital and operational improvements that range from constructing new energy-efficient facilities; decommissioning underutilized and less efficient buildings and spaces; re-commissioning existing building systems for current uses; and optimizing equipment operations.
Agilent has completed over 50 energy and water conservation
projects including:
A project on the Santa Clara campus included a new modulating
boiler controller, boiler plant re-piping and upgrades, which
generated 4% in gas savings, an average of 453,017 therms, converted
to 663,669 kWh, reducing emissions by 328 tons CO2-equivalent
annually.
Also in Santa Clara, Agilent added a recirculating system that helped the company save 493,714 gallons of water annually. At its Colorado Springs campus, Agilent improved its AHU duct pressure control (average fan speed for AHUs reduced 30-45% by reprograming with duct static pressure control). This initiative reduced energy consumption by 1.65 million kWh annually, and emissions by 817 tons CO2-equivalent. Also, by implementation of the swamp cooler hooked up to the AHUs, it saved 788,400 gallons of water annually.
The Agilent Hachioji campus in Japan implemented various operational improvements, including optimizing the chilled water supply temperature and cooling tower fans operational temperature. The site changed the operation of individual HVACs depending on room temperature. These operational control initiatives reduced loading pressures of equipment and conserved 153,409kWh of electricity consumption annually, avoiding 76 tons CO2-equivalent.
Various operational improvements were implemented at Agilent's Manesar campus in India, including reducing pump run time and reducing lighting usage. Onsite lighting and operational controls saved 101,598 kWh of electricity annually, saving 50 tons CO2-equivalent. Also, by installing state-of-the-art aerators in the campus cafeteria, the kitchen now saves 1,017 cubic meter of water consumption annually.
In FY14, our net energy conservation (for sites included in this report) was 1.15% and water conservation was 1.08% against 2% conservation goals for both energy and water. (This data uses FY13 total energy spend as a baseline).
Waste Management
Agilent's FY15 waste management plan is to establish a third-party waste vendor facility review process to reduce environmental risks from hazardous waste disposal
Agilent recognizes ISO 26000 as a reference document that provides guidance on social responsibility. Agilent aligns with ISO 26000 standards as part of our social responsibility practices. As such, Agilent's environmental policies, programs, and procedures align with ISO core subjects: Environment 6.5 and Organizational Governance 6.2.
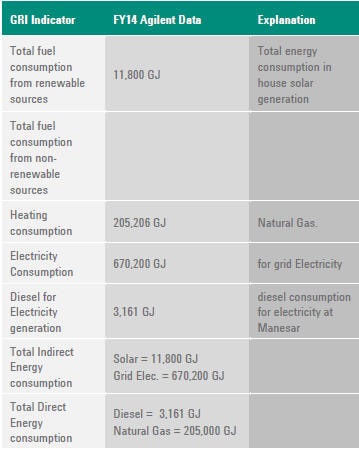
G4-EN3
ENERGY CONSUMPTION WITHIN ORGANIZATION
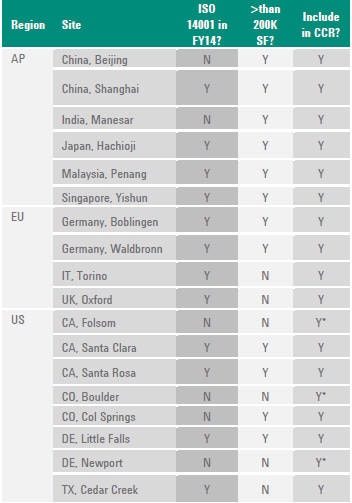
Worldwide Energy Consumption 2014
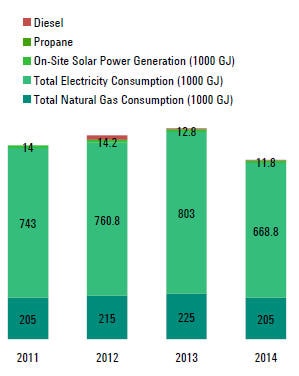
(The data provided for energy and water has been attested by TruCost)
Notes:
- US Energy Information Agency International Electricity Emissions Factor by Country, 1999–2002 were utilized for all non-U.S. facilities. Details are available at http://www.eia.gov/oiaf/1605/emission_factors.html
- For US facilities, new factor for US Grid electricity. Ninth edition with year 2010 data (Version 1.0) Details available at http://www.epa.gov/cleanenergy/energy-resources/egrid/index.html.
- For stationary fuel consumption (i.e. natural gas) DEFRA 2014 standards are used. Details are available at http://www.ukconversionfactorscarbonsmart.co.uk/.
G4-EN4
ENERGY CONSUMPTION OUTSIDE THE ORGANIZATION
Agilent energy consumption outside the company is grouped in three distinct categories:-
- Goods and services (Includes procurement, upstream and downstream transportation and distribution. Most energy consumption in this category is captured in our freight and logistics vendor emissions reported under G4-EN-17.
- Business travel and employee commuting: Energy consumption for business travel is captured under G4-EN-17. Agilent plans to expand employee commuting data reporting to include other county locations where Agilent operates. For this report, under G4-EN-17 we are only reporting US employee commuting.
- Use of sold products and end life treatment of products: Description of our efforts to reduce energy consumption of our products is reported under G4-EN-7. Details about options available to our customers for end life treatment of our products are given under G4-EN-27.
G4-EN5
ENERGY INTENSITY
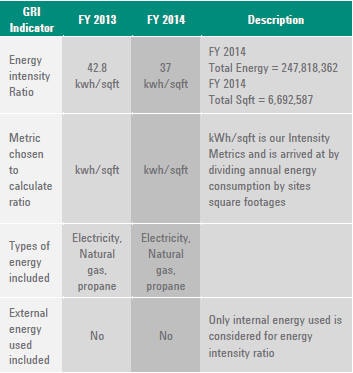
G4-EN6
REDUCTION OF ENERGY CONSUMPTION
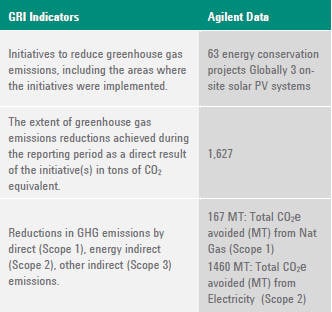
Total reduction in energy consumption for FY 2014 was 11,692 GJ. We focused on electricity and natural gas when calculating reduction in total energy consumption. For energy reduction calculation, Agilent only considers annualized energy efficiency improvements implemented in reporting fiscal year and not prior years.
Agilent's net energy conservation (for sites included in this report) was 1.15 percent against 2% conservation goals for energy. (Calculation is based on using FY13 total energy spend as a baseline).
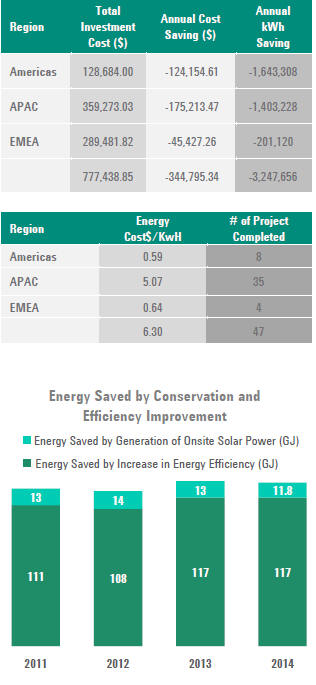
G4-EN7
REDUCTION IN ENERGY REQUIREMENTS OF PRODUCTS AND
SERVICES
Agilent is working on improving the energy efficiency of selected
products/product families including instruments with high energy
consumption.
Agilent has worked on assessing energy efficiency of
several types of products by using customer based feedback and
metrics. By identifying energy efficiency features, we are able to
increase energy efficacy of our products. Most of the energy savings
achieved so far are based on to two key factors:
- The increased type and volume of tests that can be conducted, thus increasing tests per watt.
- Enhanced existing product features, thus bringing more measurement capabilities to the same product footprint.
Agilent's concentration on handheld and portable instruments places
a focus on energy efficiency:
Next-generation products are using
key new technology that greatly improves performance per watt of power
supplied. Agilent puts significant power management design efforts
into its portable products to achieve power, heat, and battery life
targets. Industry and regulatory requirements on the power supplies
for our portable products have also increased power supply efficiency.
G4-EN8
TOTAL WATER WITHDRAWAL BY SOURCE
Total volume of water from water utilities (1,000 m3) = 848.04
Wastewater purchased from other organizations includes 50,182 m3 of
"NEWater," purchased at the Singapore site which is reclaimed water
produced by the local water board. It consists of wastewater that has
gone through water-treatment processes including purification and UV
technology. This amount is included in the "water withdrawn" totals
below.
Water withdrawn from water utilities per region (1,000 m3):
- Asia Pacific - 425.102
- Europe - 36.544
- USA - 386.392
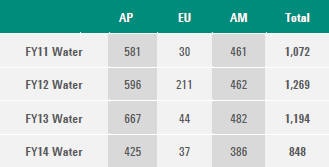
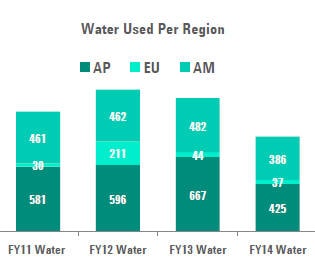
G4-EN9
WATER SOURCES SIGNIFICANTLY AFFECTED BY
WITHDRAWAL OF WATER
Most of our manufacturing site water comes directly from the city water supply. However, the following sites draw some water from the local aquifer: Manesar, India; Torino, Italy; Hachioji, Japan; Santa Rosa, USA. Of those sites, Manesar, India is the only site considered to have a water source potentially affected by withdrawal of water. Water withdrawal at Manesar, India was 22.62 (100 m3) during FY14.
G4-EN10
PERCENTAGE AND TOTAL VOLUME OF WATER RECYCLED
AND REUSED
The only site that currently uses recycled water is Santa Rosa,
USA, which has an onsite wastewater treatment facility. During the
reporting period, the Santa Rosa site recycled 56.79 (1,000 m3) water.
Agilent spin off its Electronics Measurement Group in 2014 and now
Santa Rosa site belongs to Keysight Technologies.
G4-EN11
OPERATIONAL SITES OWNED, LEASED, MANAGED IN, OR
ADJACENT TO, PROTECTED AREAS AND AREAS OF HIGH BIODIVERSITY VALUE
OUTSIDE PROTECTED AREAS
Not applicable. Agilent manufacturing sites are not located in protected areas or areas of high biodiversity value.
G4-EN12
DESCRIPTION OF SIGNIFICANT IMPACTS OF
ACTIVITIES, PRODUCTS, AND SERVICES ON BIODIVERSITY IN PROTECTED AREAS
AND AREAS OF HIGH BIODIVERSITY VALUE OUTSIDE PROTECTED AREAS
Not applicable. Agilent manufacturing sites are not located in protected areas or areas of high biodiversity value.
G4-EN13
HABITATS PROTECTED OR RESTORED
Not applicable. Agilent manufacturing sites are not located in habitat-protected areas or restored areas.
G4-EN14
TOTAL NUMBER OF IUCN RED LIST SPECIES AND
NATIONAL CONSERVATION LIST SPECIES WITH HABITATS IN AREAS AFFECTED BY
OPERATIONS, BY LEVEL OF EXTINCTION RISK CO2
Not applicable. Agilent manufacturing sites are not located in habitat-protected areas or restored areas.
G4-EN15
TOTAL DIRECT GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS BY WEIGHT
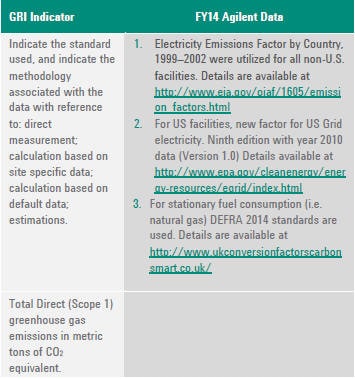
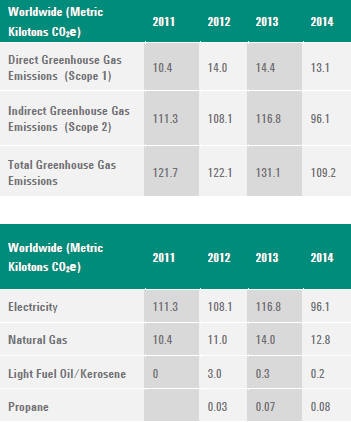
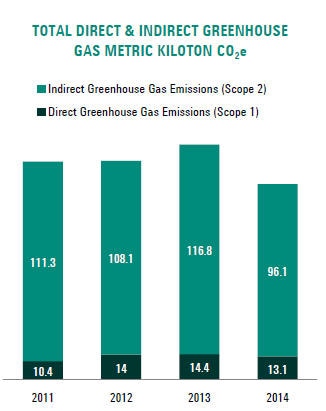
G4-EN16
ENERGY INDIRECT GREENHOUSE GAS (GHG) EMISSIONS (SCOPE 2)
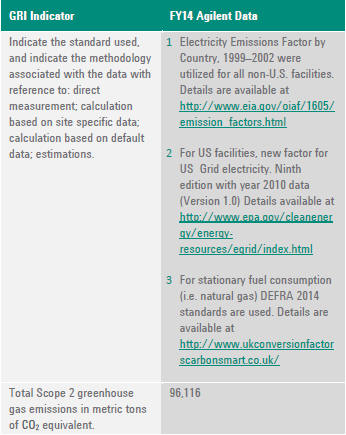
G4-EN17
OTHER RELEVANT INDIRECT GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS BY WEIGHT
(SCOPE 3)
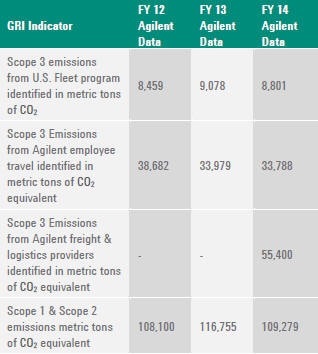
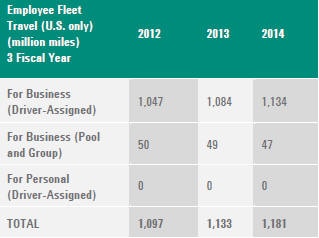
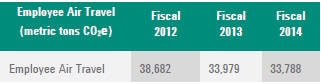
G4-EN18
GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS INTENSITY
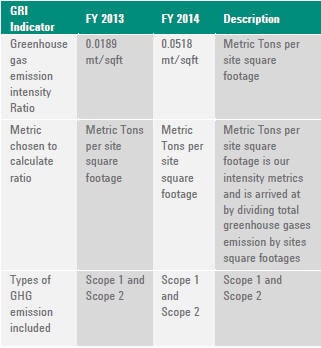
G4-EN19 REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS
G4-EN20
EMISSIONS OF OZONE-DEPLETING SUBSTANCES
Agilent does not use, produce, import, or export Ozone Depleting Substances (ODS) prohibited under the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer.
Agilent Technologies eliminated chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), carbon tetrachloride, and 1,1,1-trichloroethane use in worldwide manufacturing processes in 1993. Agilent has also eliminated Class I ODSs in its air conditioning systems, process chillers and environmental chambers. ODSs are banned from Agilent products. There are no Agilent products that need the ODS labeling required by 42 U.S.C. 7671j (b), (c), and (d) and 40 CFR Part 82, Subpart E. Procurement practices are in place to prevent the inadvertent reintroduction of ODSs into processes where they have been eliminated.
Agilent Technologies also has a program to conserve, recycle and prevent emissions of Class I ODSs and Class II ODSs used in Agilent owned equipment in its facilities worldwide.
G4-EN21
NOX, SOX, AND OTHER SIGNIFICANT AIR EMISSIONS BY TYPE
AND WEIGHT
Currently we are unable to report on these numbers.
G4-EN22
TOTAL WATER DISCHARGE BY QUALITY AND DESTINATION
In
FY14, Agilent did have water discharge from our facilities - planned
and unplanned. No chemicals laden water is discharged from Agilent
facilities; such water is handled as hazardous waste.
G4-EN23
TOTAL WEIGHT OF WASTE BY TYPE AND DISPOSAL METHOD
The data represents waste and disposal for fiscal year 2014 (Nov 13 - Oct 14) and includes both solid and hazardous waste. Agilent's target for FY2014 was based only on solid waste diversion rates and our solid waste diversion for FY 2014 was 81.9%. This exceeded the composite company-wide target by 3%.Hazardous Waste -- There was no target for hazardous waste. However in FY14, 52% of hazardous waste was treated, 4% was incinerated, 42% was recycled, and only 1% was landfilled.


Notes:
- Total waste produced is calculated by adding total chemical waste and total solid waste tonnage.
- This year total waste calculated was based on financial year (November 2013 – October 2014).
- Chemical waste refers to chemical materials designated for final disposition that exhibit characteristics that are hazardous or dangerous per local regulatory requirements. This includes materials that are shipped offsite for treatment, recycling, incineration, and landfill; and excludes electronic waste. Solid waste refers to waste that is not included in chemical waste or excess electronic equipment (e.g., garbage/trash, paper, cardboard, glass, and furniture and construction debris).
- Electronic equipment includes personal computers, computer monitors, miscellaneous electronic test and manufacturing equipment, obsolete electronic equipment, telephones, and spare or unused products from manufacturing. Waste from electronic equipment in FY14 was 197 metric tons, which was recycled.
- Electronic equipment—recycled: electronic equipment that is sent directly to an electronic recycler with the intent of recycling the equipment's components, sub-components, or material (e.g., precious metals). Agilent requires that recyclers dispose of all electronic equipment, components, and subcomponents according to state and local legal requirements.