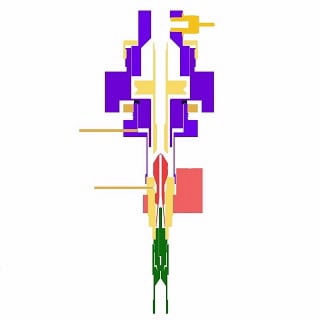
Operating Principle
An FID detects most organic compounds while exhibiting little to no response for the carrier gas. A mixture of approximately 1:10 hydrogen:air creates a continuous flame that combusts samples as they exit the GC column. One of the combustion products under these flame conditions is a hydronium ion (CHO+), which is attracted to a polarized collector, creating an ion current that is measured by an electrometer. This creates a mass-based response with a very wide dynamic range.
Theory & Operation and Troubleshooting courses are available at Agilent University.