Mitochondrial Fuel Flexibility XF Mito Fuel Flex test
What are the key mitochondrial fuels and why are they important?
In living cells, most of the energy produced is derived from three fuel sources: glucose, glutamine, and fatty acids. Fuel pathways, the biochemical processes that convert these substrates into metabolites that are oxidized in the mitochondria, are used at different rates to control a wide variety of biological processes including energy production, proliferation, and differentiation.
Which Agilent Seahorse Assay can I use to look at fuels?
The Agilent Seahorse XF Mito Fuel Flex Test is a comprehensive method for measuring mitochondrial fuel usage in live cells. The Seahorse XFp and XF Mito Fuel Flex Test Kits, used in combination with an Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer, measures the dependency, capacity, and flexibility of cells to oxidize the three key mitochondrial fuels:
1. Glucose
2. Glutamine
3. Fatty acids
1. Glucose
2. Glutamine
3. Fatty acids
Why should I do this test?
The Agilent Seahorse XF Mito Fuel Flex Test provides a rapid, label-free solution for studying substrate metabolism. With the Seahorse XF Mito Fuel Flex Test, you can measure fuel pathway preference AND compensation by sequentially modulating all three key pathways in one assay. This functional measure of fuel pathway flexibility can only be performed with Agilent Seahorse XF technology.
How would I use it in my research?
Mitochondrial access to fuels impacts a wide variety of biological processes. Using the Seahorse XF Mito Fuel Flex Test you can:
• Identify fuel dependencies to uncover cancer cell vulnerabilities
• Explore how fuel preferences lead to cell fate decisions for differentiation and immune cell activation
• Determine whether/how cells can adjust fuel oxidation to match nutrient availability while meeting energy demand
• Distinguish metabolic adaptations due to genetic changes vs. those that take place due to nutrient deprivation
• Identify fuel dependencies to uncover cancer cell vulnerabilities
• Explore how fuel preferences lead to cell fate decisions for differentiation and immune cell activation
• Determine whether/how cells can adjust fuel oxidation to match nutrient availability while meeting energy demand
• Distinguish metabolic adaptations due to genetic changes vs. those that take place due to nutrient deprivation
See what research is currently being conduced using the XF Mito Fuel Flex Test by referencing the Cell Analysis Cell Reference Database.
How does the Seahorse XF Mito Fuel Flex Test work?
The Seahorse XF Mito Fuel Flex Test works with any Seahorse XF Analyzer to determine the rate of oxidation of a given fuel by measuring mitochondrial respiration [the oxygen consumption rate, OCR] of cells in the presence or absence of fuel pathway inhibitors. Initial inhibition of one pathway measures how dependent the cells are on that particular fuel source to meet energy demand. Using a combination of inhibitors measures cells' capacity and flexibility in meeting energy demand. The Seahorse XFp and XF Mito Fuel Flex Test Kits contain all 3 pathway inhibitors (UK5099, BPTES and Etomoxir) required to determine the dependency, capacity, and flexibility of cells for glucose, glutamine and fatty acids, respectively. The Report Generator automatically converts the oxygen consumption rate (OCR) values acquired during the assay into a percent Dependency and Flexibility for each fuel and condition tested relative to all 3 major fuel pathways.
See more information on the Agilent Seahorse XF Mito Fuel Flex Test Kit.
See more information on the Agilent Seahorse XF Mito Fuel Flex Test Kit.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
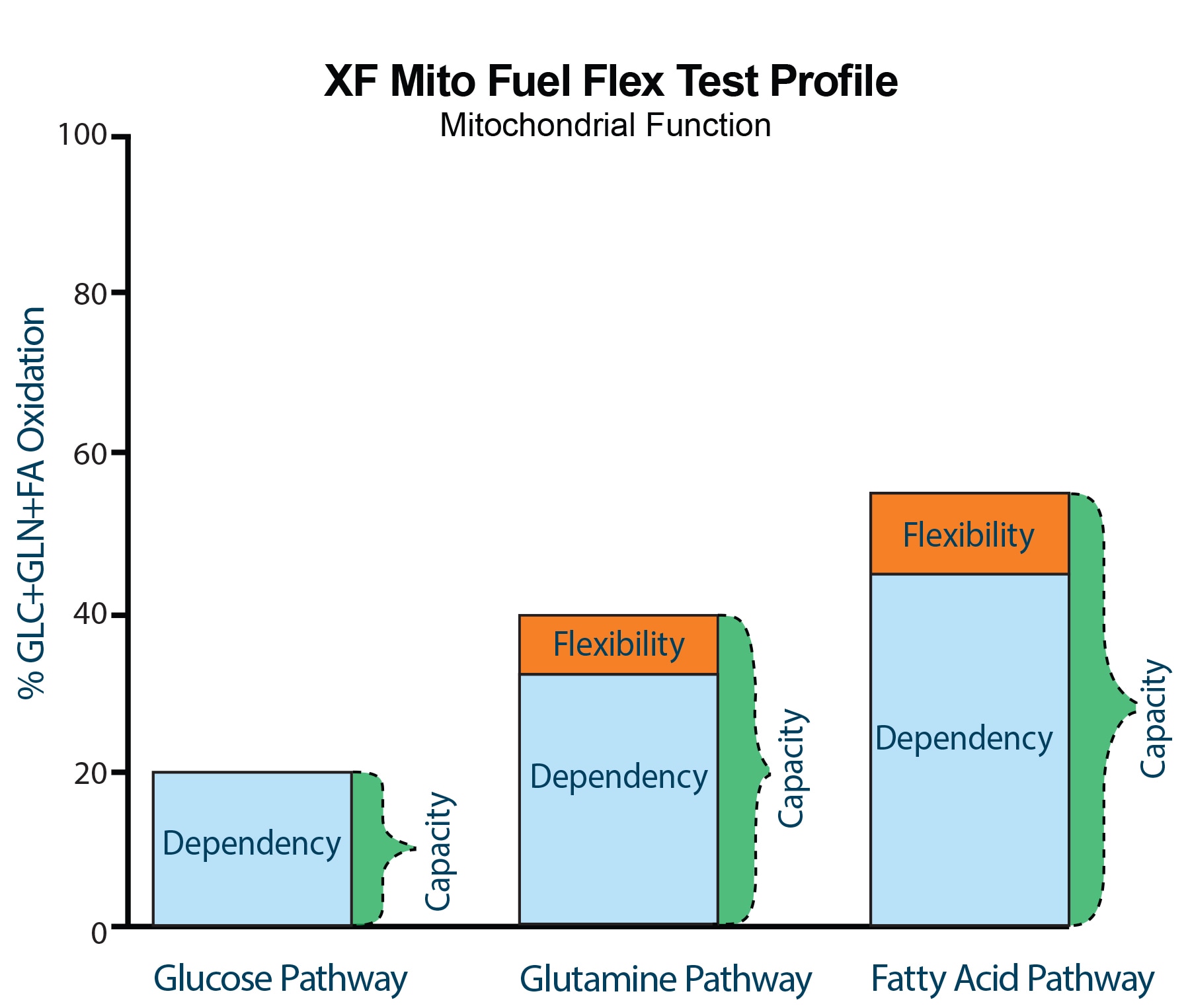
Dependency is the measurement of a cells requirement for a specific fuel to meet metabolic demand.
Capacity is the measurement of their ability to use a specific fuel to meet energy demand.
Flexibility is the difference between the amount they need and the amount they could use (capacity minus dependency).