Access Agilent eNewsletter, November 2013
>> Update My Profile | Subscribe to Access Agilent | Article Directory

A PEEK inside Agilent Bio-inert capillaries
By Katja Kornetzky
Agilent Product Manager, LC Supplies
In bio-chromatography, capillaries and connectors must be inert to ensure the lowest interaction with protein samples. Many proteins tend to interact with metals. For instance, many chelating proteins are identified and some enzymatic processes use metal as a catalyst. Other sensitive compounds tend to degrade in the presence of iron. Capillaries must also be highly robust to withstand harsh solvent conditions, such as those associated with clean in place (CIP) procedures in which strong acids or bases are employed. Additionally, high salt concentrations used in ion-exchange chromatography can precipitate at contact surfaces and lead to the formation of rust on steel components.
 Enlarge
Enlarge
Figure 1. Metal release of different LC systems after flushing with various mobile phases.
 Enlarge
Enlarge
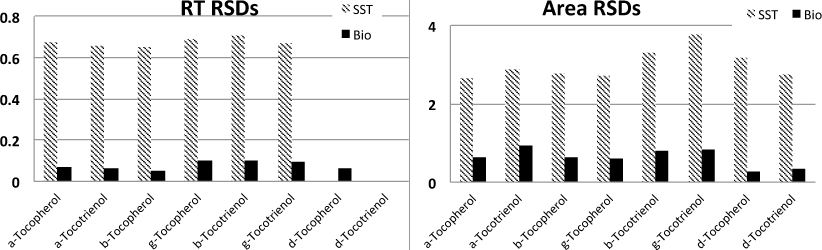
Figure 2. In the analysis of tocopherol, Agilent bio-inert PEEK/stainless steel capillaries provide a 10x improvement in retention time (left) and area (right) compared to stainless steel alone.
 Enlarge
Enlarge
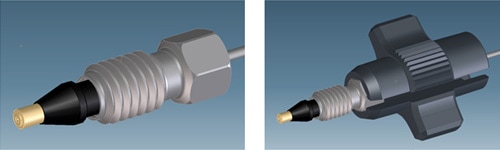
Figure 3. The robust bio-inert UHP-FF fitting (left) does not apply any twisting movement to the capillary during tightening. The ‘finger tight’ wrench (right) enables easy tightening.
The capability to withstand high operating pressures
Unfortunately, metal-free PEEK capillaries can only withstand pressures up to 300 bar. Even then, flexibility is compromised. To meet the growing need for bio-inertness, robustness, and higher operating pressures, Agilent has engineered a bio-inert capillary, comprising a PEEK liner clad with high-strength stainless steel to withstand pressures of up to 600 bar. This same technology is used in Agilent capillary fittings – providing a strong, metal-free, capillary/connector flow path for bio-inert applications.
Metal-free solutions to avoid corrosion
Constructed internally from PEEK, Agilent Bio-inert capillaries are suitable for the complete pH range from 1 to 14. The stainless-steel cladding enables use with pressures up to 600 bar, far exceeding the 300-bar pressure limit range of PEEK alone.
Only Agilent offers a metal-free sample flow path UHPLC system, in the 1260 Infinity Bio-inert Quaternary LC. Other systems use metal alloys that can lead to the formation of protein complexes and higher corrosion [1]. Figure 1 shows the superiority of Agilent Bio-inert capillaries in limiting the release of metals from LC systems.
Another application challenge is vitamin E or tocopherol, which degrades in the presence of iron. Conventional analysis with stainless steel LC systems leads to peak tailing and even loss of sample. With an Agilent 1260 Infinity Bio-inert Quaternary LC and its Bio-inert capillaries, tocopherol does not degrade. The result is a 10x improvement in retention time and area precision [2]. Figure 2 shows the details.
Easy fit without stress
The mechanically interlocked PEEK tip of the capillary is highly resistant to lateral or rotational tension, eliminating torque at the capillary, while tightening the fitting. A slip-on wrench for gripping the top of the fittings makes it easy to tighten them by hand (Figure 3).
Connections for all applications
Agilent PEEK/stainless steel capillaries are the arteries and veins of a 1260 Infinity Bio-inert Quaternary LC. Agilent offers a wide range of capillaries for all applications providing high performance connections from raw sample to analytical result. The Agilent capillary selection guide features the full portfolio and provides comprehensive advice on choosing the best capillary for a particular use.
The combination of Agilent’s BioHPLC columns with the 1260 Infinity Bio-inert Quaternary LC is a superior solution for improvements in performance, sensitivity, reliability, and productivity. It’s the system of choice for aggregation analysis, charge variant analysis, deamidation, and peptide mapping. This solution provides a robust, reliable instrument along with exceptional column performance that directly translates into faster, more confident results.
For a comprehensive overview of the advantages offered by the Agilent Bio-inert system, please see the Bio-inert LC brochure.
References
- S. Schneider. “Determination of low-metal release from the Agilent 1260 Infinity Bio-inert Quaternary LC system using ICP-MS.” Application note, Agilent Technologies, Inc. Publication number 5990-9352EN (2011).
- S. Schneider. “Quality Analysis of Virgin Olive Oils – Part 4”. Application note, Agilent Technologies, Inc. Publication number 5991-2180EN (2013).
>> Update My Profile | Subscribe to Access Agilent | Article Directory